로타바이러스 감염병 백신 예방접종, Rotavirus infection immunization
Please visit ” 0~18세 소아청소년 권장 기본 예방접종 스케줄 Recommended immunization schedule for 0~18 year old (2021 in the USA) (1) 참조”Please visit “Recommended immunization schedule for 0~18 year old (2021 in the USA) for ENGLISH INFORMATION” |
| 로타바이러스 감염 백신 예방접종의 개요 |
- 로타바이러스는 소아청소년들, 특히, 영유아들의 위장관에 감염되어 설사, 복통, 탈수, 구토, 열 등의 증상을 동반하는 바이러스성 위장염을 일으킬 수 있는 가장 흔한 바이러스의 일종이다.
- 1998년에 로타쉴드(Rotashield vaccine) 예방접종 백신이 개발되어 로타쉴드 백신으로 로타바이러스 감염성 위장염을 예방접종했다.
- 그러나 로타쉴드 백신으로 예방접종 받았던 소아청소년들의 50,000~100,000명 중 1명꼴로 장중적증이 발생됐었다.
- 1999년 이후부터 로타쉴드 백신 예방접종을 더 이상 권장하지 않았다. 그 후 새로운 연구결과로 2006년 2월에 로타바이러스 위장염을 예방할 수 있는 새 백신 “RotaTeq(Rotavirus Vaccine, Live, Oral, Pentavalent)”이 새로 개발되었고 2010년에 Rotrix 백신이 새로 개발됐다.
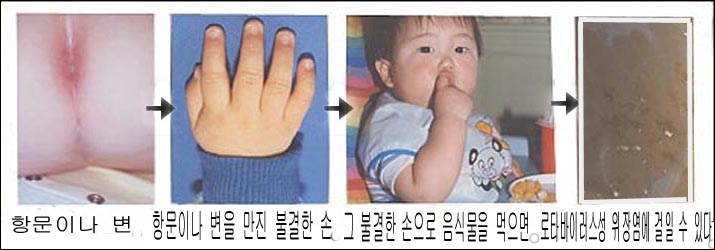
사진 4-13. 로타바이러스 위장염에 걸리는 경로.Copyright ⓒ 2011 John Sangwon Lee, MD, FAAP
| 로타바이러스 감염 백신 예방접종의 방법 |
-
RotaTeq 백신(PRV/Pentavalent rotavirus vaccine)을 생후 2, 4, 6개월에 1, 2, 3차 접종, 총 3차 접종받아 로타바이러스 감염으로 생기는 위장염을 예방해 주도록 권장하고 있다.
-
Rotrix 백신으로 1차, 2차 접종해서 예방접종 받는다.
- 로타바이러스 예방 접종은 모든 영아들에게 접종하는 기본 예방 접종이다.
- 권장한 대로 생후 2, 4, 6개월에 각각 1, 2, 3차, 총 3차 접종해 주지 않았을 때는 1차 RotaTeq 백신은 적어도 생후 6~12개월에 접종해 주고, 그 다음 2차 예방접종은 1차 접종해 준 후 6~12주에 접종해주고 3차 접종은 적어도 생후 32주 이전에 접종해주라고 권장한다. 소스: AAP news 3/2017, p27
| 로타바이러스 감염 백신 예방접종의 부작용 |
- RotaTeq (Rotavirus Vaccine, Live, Oral, Pentavalent)백신으로 예방접종을 받으면 심한 로타바이러스 위장염이 거의 100% 예방된다.
- 경미하게 열이 날 때도 예방접종을 받을 수 있고
- 모유를 먹는 영유아도 RotaTeq 백신으로 예방접종받을 수 있다.
- 부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다-소아가정간호백과-제 7권 소아청소년 감염병-로타바이러스 위장염 참조)
출처 및 참조문헌
- Red Book 32nd Ed 2021-2024
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제1권 소아청소년 응급 의료
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제2권 소아청소년 예방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제3권 소아청소년 성장 발육 육아
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제4권 모유,모유수유, 이유
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제5권 인공영양, 우유, 이유식, 비타민, 미네랄, 단백질, 탄수화물, 지방
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제6권 신생아 성장 발육 육아 질병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제7권 소아청소년 감염병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제8권 소아청소년 호흡기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제9권 소아청소년 소화기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제10권. 소아청소년 신장 비뇨 생식기 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제11권. 소아청소년 심장 혈관계 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제12권. 소아청소년 신경 정신 질환, 행동 수면 문제
- www.drleepediatrics.com제13권. 소아청소년 혈액, 림프, 종양 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제14권. 소아청소년 내분비, 유전, 염색체, 대사, 희귀병
- www.drleepediatrics.com제15권. 소아청소년 알레르기, 자가 면역질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제16권. 소아청소년 정형외과 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제17권. 소아청소년 피부 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제18권. 소아청소년 이비인후(귀 코 인두 후두) 질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com제19권. 소아청소년 안과 (눈)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제 20권 소아청소년 이 (치아)질환
- www.drleepediatrics.com 제21권 소아청소년 가정 학교 간호
- Red book 29th-31st edition 2021
- Nelson Text Book of Pediatrics 19th- 21st Edition
- The Johns Hopkins Hospital, The Harriet Lane Handbook, 22nd edition
- Childhood Emergencies in the Office, Hospital and Community, American Academy of Pediatrics
- Emergency Medical Service for Children, By Ross Lab. May 1989. p.10
- Emergency care, Harvey Grant and Robert Murray
- Emergency Care Transportation of Sick and Injured American Academy of Orthopedic Surgeons
- Emergency Pediatrics A Guide to Ambulatory Care, Roger M. Barkin, Peter Rosen
- Immediate care of the acutely ill and injured, Hugh E. Stephenson, Jr
- The Critically Ill Child, Diagnosis and Management, Edited by Clement A. Smith
- Emergency Medical Services for Children: The Role of the Primary Care Provider, America Academy of Pediatrics
- Quick Reference To Pediatric Emergencies, Delmer J. Pascoe, M.D., Moses Grossman, M.D. with 26 contributors
- Manual of Emergency Care
- 응급환자관리 정담미디어
- 소아가정간호백과–부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다, 이상원
- Neonatal Resuscitation American heart Association
- Neonatology Jeffrey J.Pomerance, C. Joan Richardson
- Pediatric Resuscitation Pediatric Clinics of North America, Stephen M. Schexnayder, M.D.
- Pediatric Critical Care, Pediatric Clinics of North America, James P. Orlowski, M.D.
- Preparation for Birth. Beverly Savage and Dianna Smith
- Infectious disease of children, Saul Krugman, Samuel L Katz, Ann A. Gershon, Catherine Wilfert
- The Harriet Lane Handbook 19th Edition
- 소아과학 대한교과서
- 제1권 소아청소년 응급의료 참조문헌과 출처
- 제2권 소아청소년 질병․안전사고 예방 참조문헌과 출처
- Other
-
Copyright ⓒ 2015 John Sangwon Lee, MD., FAAP
“부모도 반의사가 되어야 한다”-내용은 여러분들의 의사로부터 얻은 정보와 진료를 대신할 수 없습니다.
“The information contained in this publication should not be used as a substitute for the medical care and advice of your doctor. There may be variations in treatment that your doctor may recommend based on individual facts and circumstances. “Parental education is the best medicine.”